In the demanding geography of artificial thermal operation, achieving maximum heat transfer effectiveness while minimizing space and energy consumption remains a consummate challenge. The finned tube heat exchanger has surfaced as a superior result for operations taking enhanced heat transfer performance, particularly when dealing with feasts or fluids with low heat transfer portions. By dramatically adding the face area available for heat exchange, these technical systems deliver effectiveness earnings that restate directly into reduced operating costs, lower outfit vestiges, and bettered process control across different artificial sectors.
The Engineering Advantage of Finned Tube Design
Finned tube heat exchangers represent an elaboration in heat transfer technology, addressing the abecedarian limitation of smooth tube designs. The addition of fins — extended shells attached to the base tube — multiplies the effective heat transfer area without proportionally adding the overall size of the outfit. This design principle proves particularly precious when heat transfer on one side of the exchanger is significantly lower than the other, a common script in gas- to- liquid or air- cooling operations.
The fins can take colorful forms, including longitudinal fins, helical fins, plate fins, or speckled configurations. Each design offers distinct advantages depending on the operation conditions. Longitudinal fins exceed in operations with implicit fouling enterprises, as their figure facilitates cleaning. helical fins give excellent heat transfer addition for clean services, while plate fin designs maximize conciseness in operations like air- cooled heat exchangers.
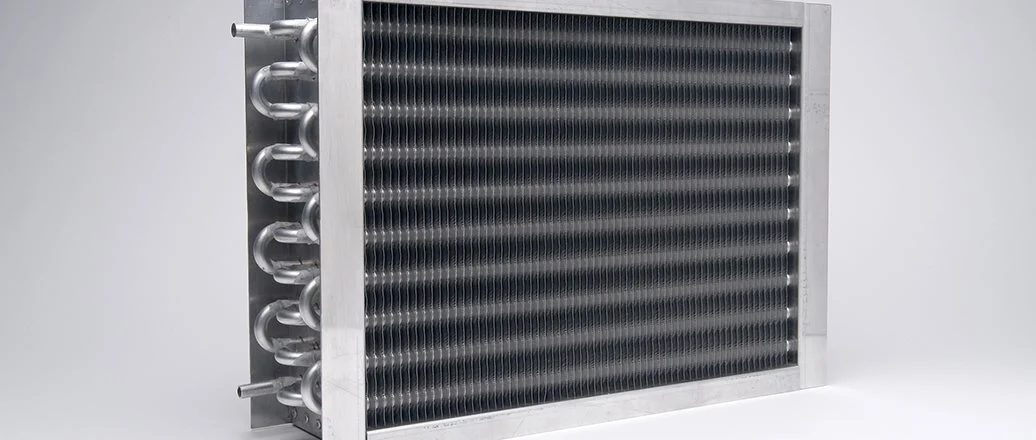
Operations Where Finned Tubes Excel
Industrial Process Cooling
Manufacturing installations across chemical processing, petrochemical refineries, and power generation shops calculate heavily on finned tube heat exchangers for process cooling operations. When cooling process fluids with air or other feasts, the low heat transfer measure on the gas side creates a tailback . Fins compensate for this limitation by furnishing extensively increased face area on the gas side, balancing the heat transfer rates and dramatically perfecting overall performance.
HVAC and Climate Control Systems
Commercial and artificial HVAC systems considerably use finned tube technology in both heating and cooling coils. The fins maximize heat transfer between refrigerants or hot water and the girding air, enabling effective temperature control with compact outfit. This effectiveness translates directly into reduced energy consumption for erecting climate control, a significant consideration given that HVAC systems generally regard for substantial portions of marketable energy operation.
Waste Heat Recovery
Industrial installations induce enormous quantities of waste heat through colorful processes. Finned tube heat exchangers grease provident waste heat recovery by efficiently transferring thermal energy from exhaust feasts to reuse fluids, boiler feedwater, or space heating systems. The enhanced heat transfer area allows effective energy recovery indeed with low- temperature differentials that would render smooth tube designs impracticable.
Compacting and sinking operations
In refrigeration systems, condensers, and evaporators, finned tubes optimize the phase change processes. The extended face area accommodates the high heat transfer rates needed during condensation and evaporation while maintaining manageable outfit sizes. This effectiveness enables further compact refrigeration systems with bettered performance characteristics.
Design Considerations for Maximum effectiveness
Fin figure and Material Selection
The effectiveness of finned tubes depends critically on fin design parameters including height, consistence, distance, and material. high fins give further face area but may witness reduced effectiveness at the fin tips due to thermal resistance along the fin length. Optimal fin distance balances increased face area against eventuality inflow restrictions and fouling vulnerability.
Material selection requires corresponding thermal conductivity with erosion resistance and mechanical strength. Aluminum offers excellent thermal conductivity and low cost, making it ideal for numerous air- cooled operations. Bobby provides superior heat transfer for refrigeration systems. Stainless sword or special blends come necessary in sharp surroundings, despite their lower thermal conductivity.
Air or Gas- Side haste Optimization
On the finned side, generally the air or gas side, haste significantly impacts performance. Advanced rapidity increase heat transfer portions through enhanced turbulence but also increase pressure drops and associated addict or cracker power conditions. Engineering analysis identifies the optimal haste that maximizes net effectiveness considering both bettered heat transfer and increased pumping costs.
Fouling Mitigation Strategies
While fins dramatically enhance clean face performance, they can also trap particulates and accumulate deposits more readily than smooth tubes. opting applicable fin configurations for the operating terrain becomes pivotal. operations with high particulate lading may profit from wider fin distance or longitudinal fin designs that grease cleaning. Regular conservation schedules and effective filtration systems cover finned shells from performance- demeaning deposits.

Performance improvement Strategies
Tube- Side Flow Optimization
The fluid flowing inside the tubes contributes significantly to overall heat transfer performance. Turbulent inflow conditions inside tubes enhance heat transfer portions mainly compared to laminar inflow. icing acceptable tube- side rapidity through proper inflow distribution and applicable tube sizing maximizes internal heat transfer, completely using the external fin improvement.
Pack Configuration and Layout
The arrangement of finned tubes within the exchanger pack influences both heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics. Inline and staggered tube arrangements each offer distinct advantages. Staggered patterns generally give advanced heat transfer rates due to increased turbulence but at the cost of advanced pressure drops. Computer modeling helps optimize tube layout for specific operations, balancing performance against functional costs.
Multiple Pass Configurations
enforcing multiple tube passes increases the effective heat transfer by allowingcounter-flow orcross-counter-flow arrangements. These configurations maintain advanced temperature differentials throughout the exchanger, perfecting thermal effectiveness. The trade- off involves increased complexity and advanced tube- side pressure drops, taking careful engineering analysis to determine optimal configurations.
Conservation and functional Stylish Practices
Sustaining peak effectiveness requires visionary conservation approaches. Regular examination of fin shells for damage, erosion, or fouling allows timely intervention before performance degrades significantly. Fin damage from mechanical impacts or erosion reduces effective face area, while accumulated dirt or natural growth creates separating layers that vitiate heat transfer.
drawing methodologies must suit the fin configuration and operating terrain. High- pressure water washing, chemical cleaning, or mechanical brushing can restore fouled shells. preventative measures including upstream filtration, defensive coatings, and biocide treatment programs reduce conservation frequence and extend outfit life.
Performance monitoring through temperature and pressure measures provides early warning of declining effectiveness. Tracking approach temperatures the difference between outlet temperature on one side and bay temperature on the other — reveals effectiveness trends. adding approach temperatures gesture fouling, inflow problems, or other issues taking attention.
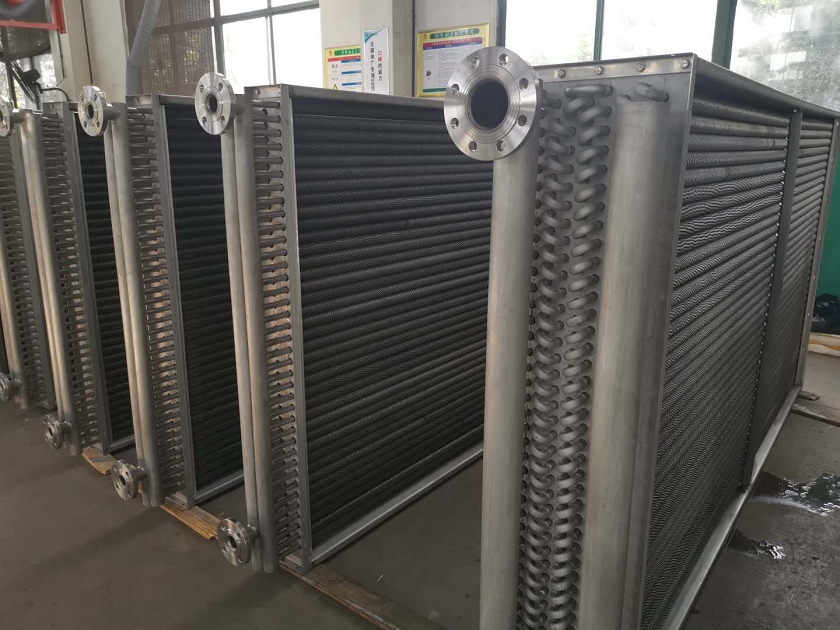

Profitable and Environmental Benefits
The effectiveness advantages of finned tube heat exchangers deliver measurable profitable returns. Reduced energy consumption directly lowers operating costs while dropped outfit sizes minimize capital expenditures and installation costs. In build operations, replacing smooth tube packets with finned tube designs can increase capacity without expanding overall outfit confines.
Environmental benefits accompany these profitable advantages. Lower energy consumption reduces hothouse gas emigrations associated with power generation or energy combustion. More effective heat recovery decreases waste heat discharge to the terrain. As diligence face adding pressure to reduce environmental vestiges, finned tube technology offers practical pathways toward sustainability pretensions.
Partnering with Endured Heat Exchanger Manufacturers
Achieving optimal performance from finned tube heat exchangers requires moxie in thermal engineering, accoutrements wisdom, and operation-specific design. Working with established manufacturers who understand the nuances of finned tube technology ensures systems are duly specified and optimized for your specific conditions. Companies with comprehensive product portfolios and deep assiduity experience can give precious guidance on opting the right heat transfer result.
Kinetic Engineering stands as a trusted mate for artificial thermal operation results, offering expansive experience in designing and manufacturing high- performance heat exchangers for demanding operations. Beyond their moxie in finned tube technology, they also give robust shell and tube heat exchanger systems for operations where that design proves further suitable. Their engineering platoon works nearly with guests to dissect process conditions, recommend optimal configurations, and deliver outfit that meets exacting performance norms.
Conclusion
Finned tube heat exchangers represent a proven technology for enhancing effectiveness in artificial thermal operation systems. Their capability to dramatically increase heat transfer face area while maintaining compact vestiges makes them necessary across multitudinous operations, from process cooling and HVAC systems to waste heat recovery and refrigeration. By understanding design principles, enforcing proper functional practices, and maintaining outfit proactively, artificial installations can realize substantial effectiveness earnings that ameliorate both profitable performance and environmental sustainability. As diligence continue seeking ways to optimize energy operation and reduce functional costs, finned tube heat exchangers will remain essential tools for achieving these objects in decreasingly competitive and environmentally conscious requests.





